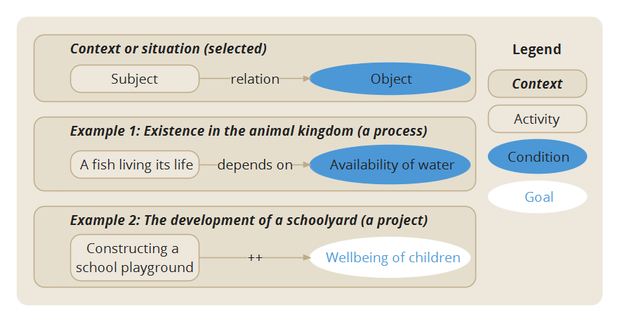
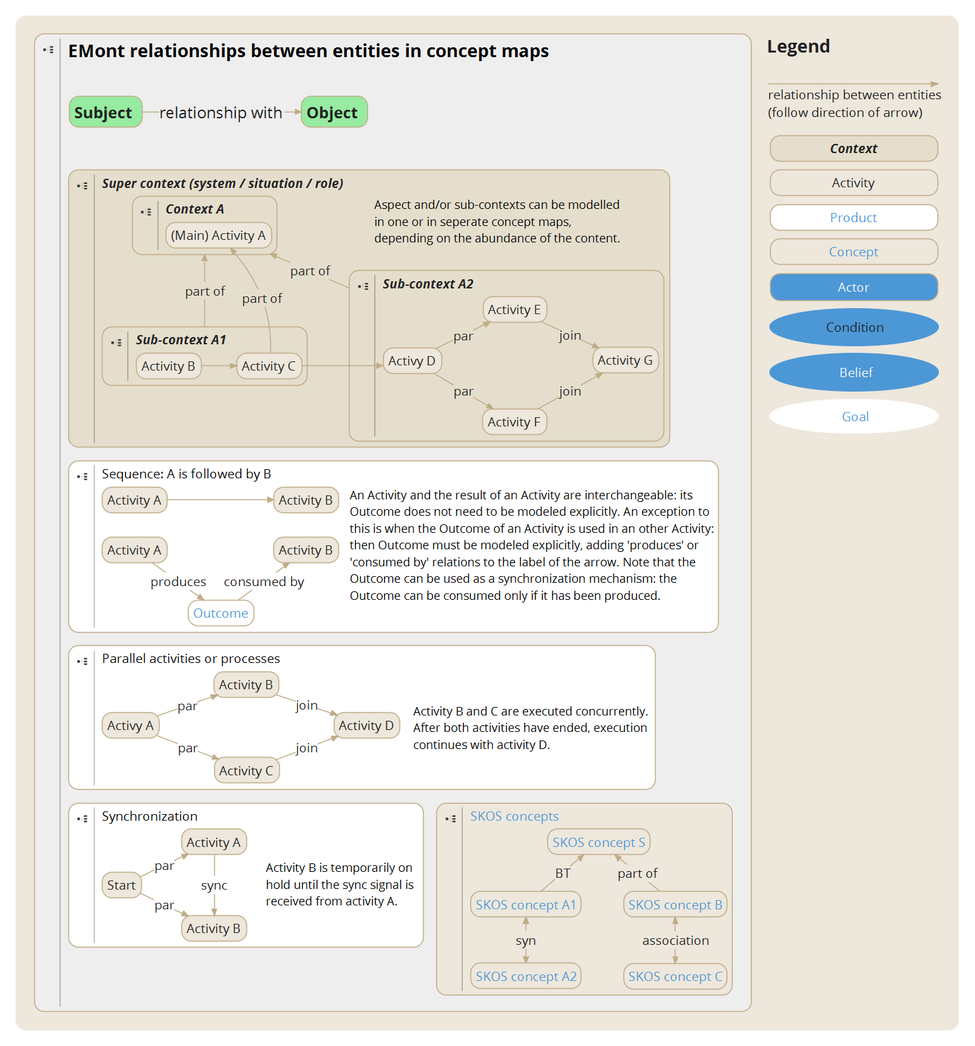
EMont (Expertise Management ontology) is a universal, common 'language' to describe and structure knowledge, expertise and (human) interactions, such as knowledge models, case studies and projects. EMont is the formal approach to appointing meaningful relationships (semantics) between Subjects and Objects ('units of knowledge'). EMont can be applied both in concept maps (visualizations of knowledge models) and at semantic websites.
(Situational specific) knowledge modeled with EMont should be structured or read like a sentence: SUBJECT =EMont relation⇒ OBJECT.
Example 1: The process of Existence: A fish living its life =depends on⇒ the availability of water. Where:
- A fish living its life is the Subject and modeled as an Activity, in this case: the natural process of life.
- Availability of water is the Object and modeled as an environmental Condition, a quantitative enabler of life.
Example 2: A construction project: Constructing a school playground =contributes positively to⇒ wellbeing of children. Where:
- Constructing a school playground is the Subject and modeled as an Activity, in this case: the execution phase of a project on the development of a schoolyard.
- Wellbeing of children is the Object and modeled as a Goal: the goal which the execution of a project on the development of a schoolyard aims to reach.
Overview of Subjects and Objects in the EMont language[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]
| Subject (or Object) | Alternative name | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| ACTIVITY | Process | Something that happens (e.g. a project related workshop or plant growth). Describe Activities with a verb. |
| ACTOR | An Actor is a human entity, e.g. a person or an organization. Actors can play a Role (modeled as a Context) or executing activities (modeled as Activities). | |
| BELIEF | Precondition | A given within a Context (can not be influenced) |
| CONCEPT | Term | Thesaurus concept (SKOS concept); SKOS = Simple Knowledge Organization System |
| CONDITION | Can be influenced within the Context, e.g. by the execution of certain processes (Activities) | |
| CONTEXT | Situation; Role of an actor / organization; System | A Context is a place where Intentional Elements (Subjects and Objects, divided into Practices and Experiences) form a consistent knowlegde system. |
| GOAL | Goal of a project or a process | |
| PRODUCT | Outcome; Input | Physical or intangible product |
Overview of official EMont relations between Subjects and Objects[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]
This matrix provides with the official semantic EMont relations. These relations have to be applied at the semantic wiki-pages and can be applied in the concept maps (for alternative relations that enhance readability of a concept map, see below).
Read this matrix like a sentence: SUBJECT =relation⇒ OBJECT.
| OBJECT ⇒
SUBJECT ⇓ |
Activity | Actor | Belief | Concept | Condition | Context | Goal | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTIVITY | part of; temporal relations: seq, par, join, sync, [conditional expression] | depends on | depends on | contributes to; depends on | contributes to | consumes; produces | ||
| ACTOR | contributes to | part of | ||||||
| BELIEF | contributes to | part of | contributes to1 | |||||
| CONCEPT | association; BT; part of; syn | |||||||
| CONDITION | contributes to | depends on1 | part of | part of2 | ||||
| CONTEXT | super context | |||||||
| GOAL | contributes to | part of | ||||||
| PRODUCT | part of |
1. Sometimes Beliefs and Conditions influence eachother directly and connecting these might enhance the readability of the concept map. According to EMont a Belief or Condition can not be connected to another Belief or Condition directly. Usually, Beliefs or Conditions can only be connected with eachother via a process (an Activity). However, in some cases we are not necessarily interested in this process, or the process is simply unknown. Then the following construction is allowed: Belief =++⇒ Condition (instead of: Belief =++⇒ Activity (unknown) =++⇒ Condition). See for example the wiki page on [[Zeegras Ecologie van zeegras VN|the ecology of sea grasses]] (in Dutch). In deze conceptmap zijn een aantal condities aan elkaar gelinkt, omdat ze elkaar beïnvloeden, bijvoorbeeld 'Troebelheid water' en 'Licht': de hoeveelheid beschikbaar licht neemt af als de troebelheid toeneemt. Hier zou je een proces of activiteit tussen moeten zetten, zoals 'absorptie', maar er is gekozen om de relatie weg te laten vanwege de duidelijkheid en omdat ze evident is.
2. A Condition can be part of an Outcome. In this case the part of relation indicates that the result of an Activity establishes the value of a related Condition. Example: the results of measurements on the availability of day light can be seen as a condition that influences plant growth. This condition can either be influenced (e.g. adding artificial light to enhance plant growth) or plant growth simply remains influenced by this condition.
Overview of alternative EMont relations[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]
This matrix provides with alternative relations to the official EMont relations in order to enhance the readability of a concept map. These alternative relations are both less and more intuitively defined, yet fully in line with EMont. These relationships are however not applied at the semantic wiki.
Read this matrix like a sentence: SUBJECT =relation⇒ OBJECT.
| OBJECT ⇒
SUBJECT ⇓ |
Activity | Actor | Belief | Concept | Condition | Context | Goal | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTIVITY | [choice; decision] | executed by | results in | |||||
| ACTOR | executes; implements | |||||||
| BELIEF | prescribes; starting point for | |||||||
| CONCEPT | NT | |||||||
| CONDITION | ||||||||
| CONTEXT | super context | |||||||
| GOAL | ||||||||
| PRODUCT | consumed by; used for |
Explanation to EMont relations[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]
The EMont relations are indicated at the Wiki-pages and used as labels in the arrows in concept maps (to semantically relating Subjects to Objects).
| EMont relation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| association | Non-hierarchical relation between Concepts, described with a verb (arrow-head in both directions). |
| BT / NT | BT = Broader term (Concept). Alternative relation: NT = narrower term |
| [conditional expression] | Path may be taken if the expression evaluates to true
Alternative relation: [choice / decision] |
| consumes | An Activity consumes an Outcome (product) |
| contributes to | Default label: ++, +, +/- (impact unknown), -, --, 0 (no impact). These values indicate the (quantitative) extent to which a Subject contributes to an Object.
Alternative relation: influences, brings about, works against, limits, etc. |
| depends on | Subject depends on an Object (e.g. an Activity depends on a Condition) |
| join | Parallel Activities coincide in and continue with an Activity. Does not need to be included in case it is obvious from the concept map. |
| par. | par. = parallel. This is a relation between Activities that are executed concurrently, originating from an Activity. |
| part of | A Subject (or Object) is part of a more generic, yet similar Subject (or Object). In case of an Experience (a case defined as a Subject) related to a Practice (a good practice defined as an Object) the EMont relation is called: instance of or alternatively: example of. This relation can also be shown by including the text bubble in another text bubble. |
| produces | An Activity produces an Outcome (product) |
| relate | Relate links knowledge structures. For example: a Guided Tour can be linked with associated Expertise (action perspectives). The relationship relate is not included in the overview of EMont relations. More information on this relationship will follow |
| seq. | seq. = sequence: a Subject is followed by an Object (usually sequential Activities).
Default label: no text in the label of an arrow. |
| syn. | syn. = synonym. The preferred Concept of these synonyms is related to another Concept. The non-preferred synonym is modeled as an alternative Concept (at the end of the knowledge model, like leaves at trees). |
| sync. | sync. = synchronizes with. Indicates that two paralel activities are synchronized. During the synchronization process information can be exchanged between the two activities. |
Zie ook
- EMont
- EMont tutorial
- HSI-relatie
- Using EMont in the right way
- Semantische relaties invullen op formulier
- Overlagingen zeedijken in relatie tot broedvogels
- infiltratiemetingen Paviljoenpolder (Fugro) en relatie met dichtheidsmetingen
- Risicobeeld oestertransporten in relatie tot mariene invasieve exoten
- Afschuiving steenzettingen en stabiliteit teenconstructie in relatie tot klemming toplaag
- Ontwikkeling morfologie Oosterschelde in relatie tot de zandhongerproblematiek