| PQR formula | |
|---|---|
| Context | Expertise Management Methodology |
| Decompositie type | IOR |
The PQR formula is the working horse of EMont. The formula stems form the Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) in which it is used as an aid to express a root definition: a statement written in a few sentences capturing the intention of someone's worldview. The PQR formula is given the central role in EMont because it captures the notion of cognitive patterns or practices concisely.
The letters P, Q and R do not stand for anything, except that they are subsequent letters in the alphabet, but they do have a special meaning:
- P - what?
- Q - how?
- R - why?
The PQR formula should read as a sentence: Do P by a Q in order to achieve R.
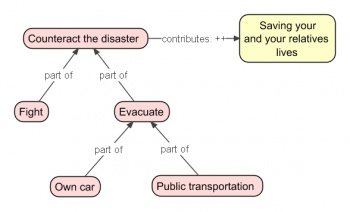
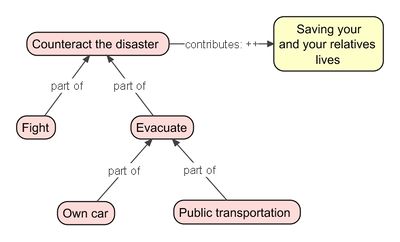
For example, if a disaster strikes, then you should counteract (P - what) to save your and your relatives lives (R - why). But the question is how do we save lives. Usually, there are several options, that is, particular ways (Q's - how's) to achieve the desired goal. One option is to fight the disaster (Q1). Another one is to evacuate the endangered area (Q2). Which one to choose depends on the circumstances. By setting up this PQR formula, we are actually describing behavioral patterns that humans use in order to deal with particular circumstances. We are touching on expertise or know-how knowledge in the sense that an expert can apply the right patterns almost without consciously thinking. By experience, an expert knows intuitively what to do in specific situations.
But don't stop here, the PQR formula can be applied recursively. A Q (a how) can be decomposed in deeper Q's (how's). To continue the disaster example, the evacuation activity can be subdivided in evacuation by car (Q21) or by public transportation (Q22). By doing so, the evacuation activity (Q2) becomes a P (a what) for its constituents. Generalizing from this example, by applying the PQR formula recursively, we can model the expert's knowledge, that is, his patterns, at any desired level of detail. Not only activities can be decomposed, the same holds for goals, which can be decomposed in sub-goals.
Intentional elements
The disaster example can be visualized as shown in the figure. This figure contains elements defined in EMont. These elements are called Intentional Elements (IE) because they are used to model the intentions of actors, organizations or systems in general. Two IEs are introduced in the example: activity and goal. These two are related by drawing an arrow between them. In EMont, these arrows have well-defined meanings. For instance, the result of an activity contributes in some way to the achievement of a goal. More formally we say:
activity →contributes: (+/- (undefined), --, -, 0, +, ++) goal
As a matter of fact, this kind of formula is called a triple and is used as basic modeling construct in the semantic web world:
subject →predicate object
A triple gives meaning to a subject by relating it to an object by means of an predicate. It should read as a sentence. Typically, subject and objects are written as nouns, and the predicate is written as a verb. In the contributes example above, the sentence reads as: a particular activity (subject) contributes in some sense, e.g., positively or negatively (predicate), to a particular goal (object). More concrete, evacuation contributes very positively to saving your live.
The contributes and the part-of predicates (relationships) are ones of the most frequently used predicates. To avoid unnecessary clutter in a diagram, no label is shown in the arrow when the context makes it clear that a part-of predicate is intended. By the same token, the word contributes is usually omitted when one of the symbols +/- (undefined), --, -, 0, +, ++ suffices for describing the contributes relationship between an activity and a goal.
A word of warning
Working on this one.
De View-Navigation (VN) pagina's.
De links naar andere pagina's.
| Produceert | |
|---|---|
| Consumeeert | |
| Onderdeel van | EMont tutorial |
| Instantie van | |
| Betreft |
Connectie.
| Connectie type | seq |
|---|---|
| Connecteert naar | Behavioral patterns |
| Conditie | |
| Opmerkingen |
De pagina's die linken naar deze pagina.
Dit element heeft geen subelementen. Naar dit element wordt niet geconnecteerd.