| Regel 27: | Regel 27: | ||
EMM = SSM + EM<sub>ont</sub> + conceptmaps + semantische wiki = een rijke leeromgeving die continu wordt verrijkt; een valorisatie-instrument waarmee waarde wordt gecreëerd (disseminatie van expertise). |
EMM = SSM + EM<sub>ont</sub> + conceptmaps + semantische wiki = een rijke leeromgeving die continu wordt verrijkt; een valorisatie-instrument waarmee waarde wordt gecreëerd (disseminatie van expertise). |
||
| − | + | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Paragraph |
{{Paragraph |
||
Versie van 20 mei 2015 om 11:20
| Going meta: managing expertise about the expertise management methodology | |
|---|---|
| Beschrijving | This is a comprehensive guide for mastering the Expertise Management Methodology. |
| Overkoepelende context | Expertise Management |
| Context type | |
Inhoud
EMM (tekst uit: Over ons)
De kennis op de DeltaExpertise-site is verkregen met behulp van, en gestructureerd aan de hand van de Expertise Management Methodologie (EMM). De Expertise Management Methodologie (EMM) is door HZ University of Applied Sciences ontwikkeld en succesvol toegepast in een aantal kennisdomeinen waaronder communitiy resilience en flood aware. EMM is geworteld in de Soft Systems Methodology (SSM). SSM biedt een raamwerk om door middel van actieonderzoek verbeteringen aan te brengen in complexe, problematische situaties. Deze situaties worden gekenmerkt door een grote hoeveelheid betrokkenen die er diverse – vaak tegengestelde – wereldbeelden op na houden. SSM verschaft de middelen om die wereldbeelden te expliciteren en vervolgens deze beelden op een gestructureerde wijze met elkaar te delen. Het doel is om gezamenlijk acties te bepalen die wenselijke en cultureel haalbare veranderingen in de problematische situatie zullen bewerkstelligen.
Voor expertise-management is een model EMont (Expertise Management ontologie) ontwikkeld waarmee de kennis van experts kan worden beschreven. Niet alleen feiten en conceptuele kennis (knowing that) wordt gemodelleerd, maar vooral ook de knowing-how kennis. De knowing-how kennis is die kennis waarmee een expert zich onderscheidt van anderen. Een expert kan de juiste theorie vaak onbewust direct op het juiste moment en op de juiste plaats inzetten. Noem het intuïtie, maar het is in feite vakmanschap die door jaren van ervaring is opgebouwd.
SSM samen met EMont maakt het mogelijk om de knowing-that en knowing-how kennis van experts boven water te halen. Dit gebeurt onder andere door middel van gestructureerde interviews waarmee de practices van een individuele expert expliciet worden gemaakt. Maar de practices van een expert hoeven niet noodzakelijkerwijs ook good practices te zijn. Het kan zijn dat een practice op sommige punten wel voldoet, maar op een aantal andere niet. De consequentie is dat practices gezamenlijk door experts moeten worden bediscussieerd om de beste elementen te combineren tot good en wellicht best practices. In dit proces kunnen ook de bad practices worden vastgesteld: de valkuilen die men behoort te vermijden. Ook het proces van gezamenlijk bediscussiëren en waarderen van practices gebeurt op een gestructureerde wijze.
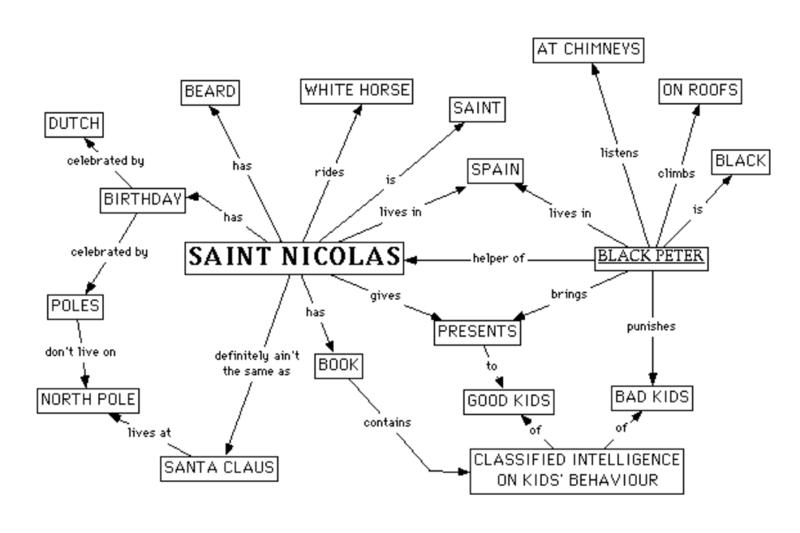
De resultaten van interviews en gezamenlijke waardering worden geschematiseerd in conceptmaps, zie onderstaande Sint en Piet conceptmap. Een conceptmap geeft een visueel inzicht in de concepten en hun onderlinge relaties in een kennisdomein. Dit verschaft een sterke basis om nieuwe kennis te integreren in bestaande kennis. De elementen die worden gebruikt in de conceptmaps zijn gedefinieerd in EMont. Hiermee worden de conceptmaps zodanig gestructureerd dat de resultaten direct in een semantische wiki (een wiki met een onderliggend model: EMont) worden gezet voor publieke disseminatiedoeleinden. Achtergrondinformatie en tips over het construeren van conceptmaps staan beschreven in een gids.
De semantische wiki kan worden gezien als een rijke leeromgeving die continu wordt verrijkt met nieuwe kennis. Deze kennis komt van diverse partijen, waaronder PBZ, HZ en andere (onderzoeks)instellingen. Door gebruik te maken van SSM wordt een proces in gang gezet waarmee kennis en expertise gestructureerd en gevalideerd gaat groeien.
EMM = SSM + EMont + conceptmaps + semantische wiki = een rijke leeromgeving die continu wordt verrijkt; een valorisatie-instrument waarmee waarde wordt gecreëerd (disseminatie van expertise).
The Expertise Management Methodology (EMM) is about utilizing expertise within and across organizations. Humans and the organizations and communities in which they participate are viewed as activity systems in the sense that they perform activities in order to achieve goals. The questions that are addressed in EMM include: what kind of activity is required to achieve goals collaboratively, how can we learn from experts, how can we deal with different opinions about how to perform an activity or can we deal with different worldviews altogether? With the systematic approach of EMM, we get a handle on answering these kind of questions.
EMM is a versatile methodology, and therefore, it is not easy to categorize the methodology. There are at least three perspectives on EMM. First, EMM can be regarded as a structured methodology to gain insight in a problematic situation. The insight in a problematic situation stems from the views on the situation by different stakeholders. Second, EMM can be used to capture knowledge and to connect it to an existing knowledge base. Used in this way, EMM is a methodology to construct a body of knowledge. Third, EMM can be seen as a methodology for networked organization development. That is, the expertise present in different organizations is used in such a way that common goals can be achieved, but at the same time, individual goals are taken into account as well.
These three perspectives are strongly related. For instance, the insights gained by investigating a problematic situations involving several organizations can be captured in a knowledge base. Group learning is facilitated in this way, thereby preventing to reinvent the wheel time and again.
EMM in relation with knowledge management
EMM differs from knowledge management in a crucial aspect. Before we can go in this matter, we must first define what knowledge management is about.
Knowledge management (KM) is the process of capturing, developing, sharing, and effectively using organisational knowledge. It refers to a multi-disciplined approach to achieving organisational objectives by making the best use of knowledge.
Source Wikipedia article: Knowledge management, retrieved: December 3, 2013.
Central in this definition are the organizational objectives and how knowledge contributes to fulfilling these objectives. This should be contrasted with the EMM approach in which we focus on expertise possessed by humans in the context of a problematic situation. This is a situation with issues which can be improved somehow, but we do not have the insights yet in the ways to do so. It is not difficult for most people to identify such situations. Typical examples include health for aging people and education in times of demographic changes. As a matter of fact, almost every situation involving several stakeholders and organizations has opportunities for improvement.
With EMM, the focus is on the issue rather than on collecting knowledge in relation with organizational objectives. When addressing a problematic situation, the organizational objectives may be questioned in the first place as a result of explicated worldviews voiced by experts. The expertise of experts is key in the process of improvement. Not only what should be done is captured in EMM, but also how experts do it. In this way, we dig deeper and go beyond organizational objectives by tapping on the potential of knowledgeable stakeholders within an organization (i.e., experts by education or by experience, or a combination of both) and utilizing the available expertise synergistically. In addition, EMM is not restricted in scope to a single organization, but can be used across organizations, even for organizations with apparent conflicting objectives, for the precise reason that we focus on the issue rather than on individual objectives. Although EMM's scope is broader than KM, EMM can also be restricted to the traditional KM approach by taking the organizational objectives as a fixed starting point.
Improving problematic situations
Two things are needed to find improvements in a problematic situation. Firstly, a methodology is required to systematically investigate the issues in a situation and where possible take action to improve. Secondly, the worldviews of knowledgeable stakeholders must be captured accurately. EMM is based on the Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) and worldviews are captured in EMM in a powerful ontology. This ontology is called the Expertise Management ontology, or EMont for short, with which human knowledge is described. SSM has proved to be an effective methodology for tackling problematic situations. By incorporating EMont in the methodology, SSM gained in power to analyze complex situations by making the expertise to improve on situations explicit. The combination of SSM and EMont forms the heart of EMM.
For the time being, while this wiki is being constructed, the reader can also refer to an introduction on EMM.
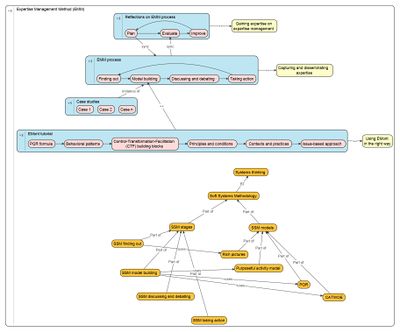
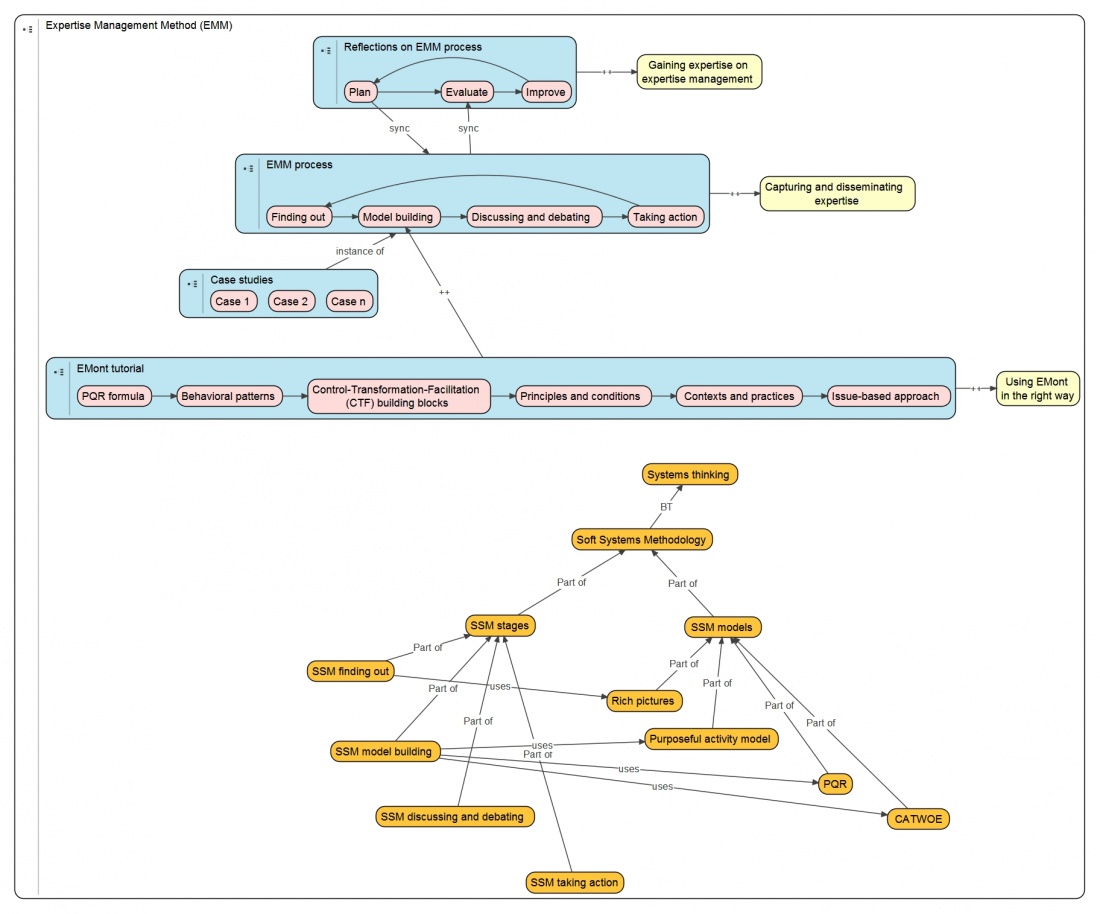
Going meta!
This wiki book is written to provide a comprehensive guide for using EMM. The material contained in this book is field tested by using EMM in practical cases, which are documented here. In fact, this book is structured using EMM principles. Good practices as well as bad practices are presented to become proficient in EMM. In short, we are going meta by demonstrating EMM by using EMM.
Click on the elements to find out what EMM is all about. (Right now, only the EMonttutorial and the elements inside it are clickable.)
De View-Navigation (VN) pagina's.
De opbouw van deze context.
- Subcontexten
- Actor
- Practices & Experiences
- Elementen
- Links tussen elementen