Oceans are generally divided in two major habitation zones: open sea and the coastal zone, also known as the littoral zone. The coastal zone extends from the high water mark till the edge of the continental shelf (till the depth of approx. 200 meters), and is characterized by warm, nutrient rich waters in which sunlight can still reach the ocean floor. Due to this, coastal ecosystems in general have a very high productivity and they also harbor 90% of all marine species. Due to close proximity of land, coastal zones can be heavily influenced by humans and human activity (Miller, 2002). Ecosystem functions, provided by the coastal zone, generate various ecosystem services that are crucial for the well-being of people, both for those situated close to the shore and those who live further inland.
Rocky shores are formed when softer rock and/or sediment are eroded to uncover harder rocks. Rocky shores consist of various types of structures, such as steep cliff-faces, rock pools and platforms, boulder and gravel fields. Organisms living on these shores have to deal with various environmental stresses - desiccation (in the intertidal zone), sand scour and wave action. They are home to numerous sessile fauna, including various barnacles, oysters, mussels and anemones. Several macro algae species, that cannot safely anchor themselves in loose sandy substrates, can be found attached to the hard rocky substrate, such as Laminaria kelp species or bladder wrack (Fucus vesiculosus), where they can create dense mats whose canopy also serves as a habitat for various coastal species. Irregularities in the rocks (pits, crevices, cracks) and various hard shelled organisms, and algae offer microhabitats and breeding or foraging grounds for a large variety of motile invertebrates, fish and sea birds (anon., 2012; Little et al., 2010).

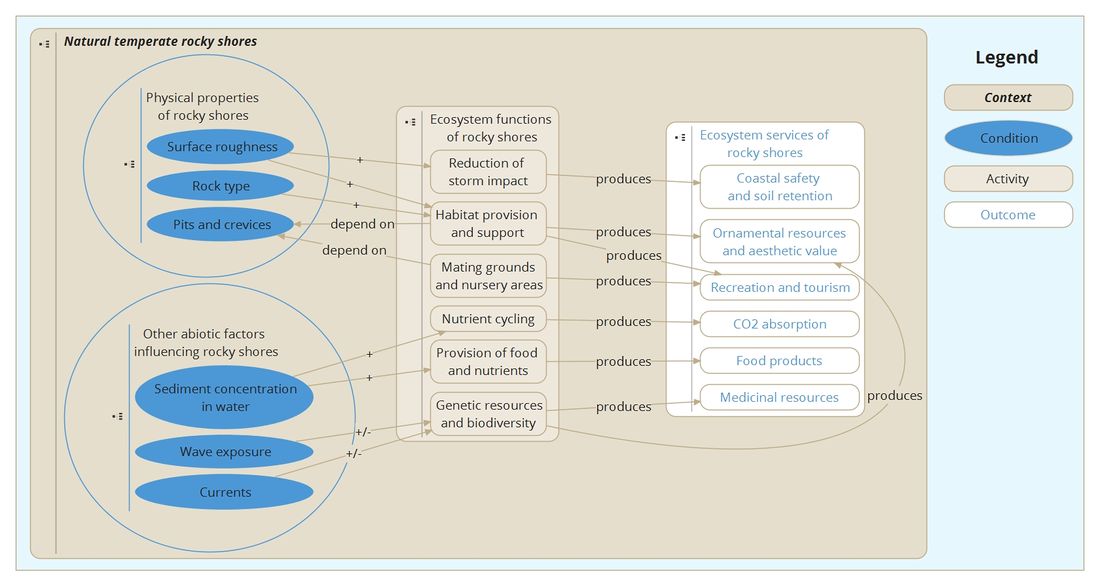
Concept map
Information collected on natural temperate rocky shores was divided into smaller sections about specific parts of the system and links connecting these part are used to show the dependencies between them, as shown in the concept map below. The nodes of the concept map are clickable and lead to separate wiki pages containing the information on them. It must be stressed, that not all relations between the elements are shown in order to make the scheme easier to read and understand.
- The Biology of Rocky Shores. 2nd Edition, Little, Colin, Williams, Gray A. and Trowbridge, Cynthia D., 28 april 2010.
- Living in the Environment. 13th Edition, Miller, G. Tyler Jr., 2002.
- Rocky shores, UK, anon., 2012.
Zie ook
- Building with Nature; from concepts to practice
- Wadden Sea Plan 2010
- The colonization by seaweed and fauna of different revetment types at Sint-Annaland, Tholen; RAAK-PRO Building for Nature final report
- The Benthic Ecosystem Quality Index (BEQI), intercalibration and assessment of Dutch coastal and transitional waters for the Water Framework Directive. Final report
- Risk analysis on the import of mussels from the Limfjord and the Isefjord (Denmark) to the Oosterschelde
- Ecosystem Services of constructed oyster reefs
- Habitat provision and support
- Oyster reefs and coastal protection
- Oesterdam sand nourishment - ecological and morphological development of a local sand nourishment
- Building with living nature; conceptual elaboration