Until present, coastal defense systems in the Netherlands have mainly been designed from a civil engineering perspective. The focus is on safety and water management. However, hard defense systems like revetments can also be viewed as artificial rocky coasts. For centuries, the construction of coastal defense systems has led to loss of nature values associated to soft sediment habitats and enlarged the extend of artificial rocky coasts (Martin et al., 2005). Yet, these newly created coasts harbor a low quality of nature values, because their design was only aimed at safety, neglecting nature values. To mitigate ecological impacts of coastal defense systems, their design may be optimized to enhance nature values and facilitate the growth of many species. The RAAK PRO-project Building for Nature aims to design revetments in such a manner that they have an added value to nature (Building for Nature project proposal, 2012 (in Dutch)). Here, we focus on the intertidal part of the dike, excluding the higher part of the dike which is never submersed and only influenced by spray. Also the riprap zone at the toe of the dike is excluded, and therefore also the larger structures like tidal pools that can be created in this zone to facilitate marine benthic communities.
Theoretical framework
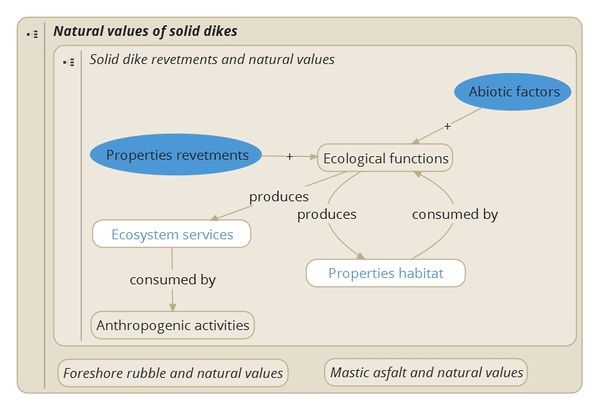
In the scheme below, the relationship is described between the properties of revetments, (other) abiotic factors and the ecological functions a revetment can provide. Depending on factors like inundation time, water salinity and temperature, a carefully designed revetment may facilitate ecological functions like the attachment and growth of seaweed, bivalves or other ecosystem engineers, which in turn create a habitat for other marine benthic species including other shellfish, anemones and small crustaceans. This may lead, as shown by the loop in the center of the figure, to more ecological functions, such as food supply for larger species of fish, crustaceans and birds like ruddy turnstones (Arenaria interpres). Ultimately, the revetment will also provide several ecosystem services, which may include the conservation of biodiversity or, on the other end, the exploitation of edible species. By clicking one of the boxes, more information is provided, including examples and references to case studies. Together this information provides the theoretical framework for different case studies that have been carried out in the Netherlands. These case studies are described based on the same scheme.
- Ecological impact of coastal defence structures on sediment and mobile fauna: Evaluating and forecasting consequences of unavoidable modifications of native habitats, Daniel Martina, Fabio Bertasib, Marina A. Colangelob, Mindert de Vriesc, Matthew Frostd, Stephen J. Hawkinsd, Enrique Macphersona, Paula S. Moschellad, M. Paola Sattaa, Richard C. Thompsonf, Victor U. Ceccherellib, november 2005.
- Project plan RAAK-PRO "Building for Nature innovatie van dijken en vooroevers", HZ University of Applied Sciences, RAAK-PRO, november 2012.
Zie ook
- Building with Nature; from concepts to practice
- The colonization by seaweed and fauna of different revetment types at Sint-Annaland, Tholen; RAAK-PRO Building for Nature final report
- Building with living nature; conceptual elaboration
- Oyster reefs and coastal protection
- Wadden Sea Plan 2010
- The Benthic Ecosystem Quality Index (BEQI), intercalibration and assessment of Dutch coastal and transitional waters for the Water Framework Directive. Final report
- 2nd newsletter - final.pdf
- Conceptual framework for Building with Living Nature. Historical perspectives on the Building with Living Nature concept.
- On the relationship between dike revetments and ecology: lessons learned for design and follow-up monitoring for asphalt covered locations
- Ecological potential of mastic asphalt for rich revetments